摘要:
一道模拟过程的题目,不难,但是有点繁琐。
题目
给你一个大小为 $m \times n$ 的整数矩阵 $grid$ ,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 都是 偶数 ;另给你一个整数 $k$ 。
矩阵由若干层组成,如下图所示,每种颜色代表一层:
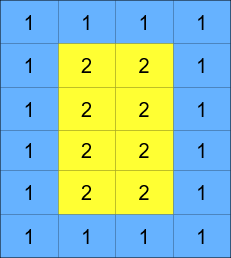
矩阵的循环轮转是通过分别循环轮转矩阵中的每一层完成的。在对某一层进行一次循环旋转操作时,层中的每一个元素将会取代其 逆时针 方向的相邻元素。轮转示例如下:
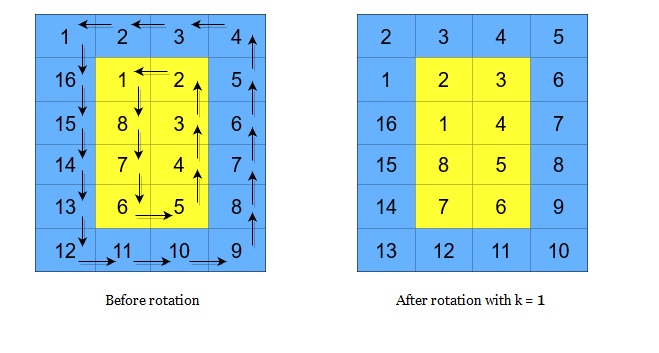
返回执行 $k$ 次循环轮转操作后的矩阵。
示例 1:
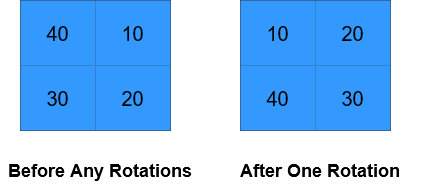
输入:grid = [[40,10],[30,20]], k = 1
输出:[[10,20],[40,30]]
解释:上图展示了矩阵在执行循环轮转操作时每一步的状态。
示例 2:
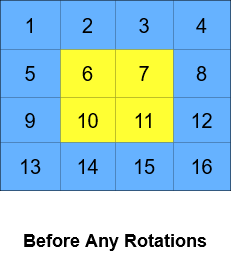
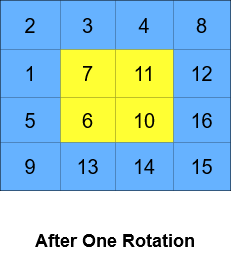
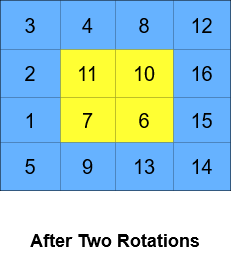
输入:grid = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12],[13,14,15,16]], k = 2
输出:[[3,4,8,12],[2,11,10,16],[1,7,6,15],[5,9,13,14]]
解释:上图展示了矩阵在执行循环轮转操作时每一步的状态。
模拟
将每一层放到一个队列中,再计算出每一层的每一位对应轮转 $k$ 次后在队列中的什么位置。
将每一层分为 $4$ 次分别处理入队,分别是上右下左,依次是行不变列增加;行增加列不变;行不变列减小;行减小列减小。
另外注意不能数组原地替换,因为前面被替换的数原本包含着最后的要替换的数的数。所以需要额外维护一个同样大小的数组。
1 | class Solution { |
模拟 + DFS
我的思路是先确定一共需要进行多少层轮转,对于每一层的每一次轮转写进行一次深搜,一共 $k$ 次,注意 $k$ 需要对一层的总数取模。
核心在于如何对指定层进行一次轮转。
深搜从每一层的左上角开始,所以我们要确定每一层的第一个数坐标。
深搜过程中到达拐点处需要改变搜索方向,所以我们需要知道每一层的长和宽。
另外我们需要对搜索过的格子进行计数,以便判断递归终止。
1 | class Solution { |
原题链接: LeetCode 1914. 循环轮转矩阵